[Python] 동시성 프로그래밍
in Python
동시성과 병렬성
동시성과 병렬성 모두 동시에 여러 가지 일을 수행한다는 뜻인데, 엄밀히 말하면 두 가지는 다르다.
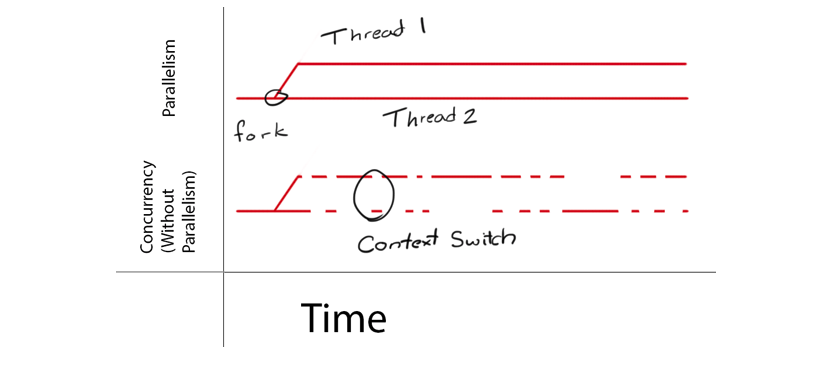
동시성 (Concurrency)
- 동시에 실행되는 것처럼 보이는 것 (논리적인 레벨)
- IO bound job 에서 사용 (서버단에서 클라이언트 요청 처리 등)
병렬성 (Parallelism)
- 실제로 동시에 작업이 처리. 작업들이 병렬적으로 수행 (물리적인 레벨)
- CPU bound job 에서 사용 (CUDA 등)
파이썬의 동시성
이처럼 동시성과 병렬성은 다른 의미를 가지고 있지만, 편의상 이 둘을 묶어 동시성 프로그래밍이라고 하겠다. 파이썬에서는 동시성 프로그래밍과 관련된 모듈이 세 가지가 있다.
threading: 스레드를 사용하는 모듈asyncio: 코루틴을 사용하는 모듈multiprocessing: 프로세스를 사용하는 모듈
이 중 정말로 동시에(병렬적으로) 작업을 처리하는 것은 multiprocessing 뿐이다. (GIL 포스팅 참고) threading 모듈에서는 운영체제가 각 스레드를 언제든지 멈추고 다른 스레드를 진행시킬 수 있다는 특징이 있다(선점형 멀티태스킹). 언제든 스위칭이 일어날 수 있기 때문에 다루기가 어렵다. asyncio 모듈은 각 태스크에 언제 스위칭 될 것인지 명시해줄 수 있다(협력식 멀티태스킹).
언제 동시성을 사용할까?
동시성을 추가한다는 것을 추가 공수가 드는 것이기 때문에 프로그램 특성을 잘 파악하고 성능 개선이 확실한 경우에만 사용해야 함
- IO 바운드 작업: 파일시스템 혹은 네트워크 연결 등이 실행 시간의 대부분을 차지. ‘대기’ 시간이 생긴다는 것이 특징.
- CPU 바운드 작업: 계산 작업이 실행 시간의 대부분을 차지
IO 바운드 작업 개선하기
순차적 버전
import requests
import time
def download_site(url, session):
with session.get(url) as response:
print(f"Read {len(response.content)} from {url}")
def download_all_sites(sites):
with requests.Session() as session:
for url in sites:
download_site(url, session)
if __name__ == "__main__":
sites = [
"https://www.jython.org",
"http://olympus.realpython.org/dice",
] * 80
start_time = time.time()
download_all_sites(sites)
duration = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Downloaded {len(sites)} in {duration} seconds")
threading 모듈
import concurrent.futures
import requests
import threading
import time
thread_local = threading.local()
def get_session():
if not hasattr(thread_local, "session"):
thread_local.session = requests.Session()
return thread_local.session
def download_site(url):
session = get_session()
with session.get(url) as response:
print(f"Read {len(response.content)} from {url}")
def download_all_sites(sites):
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
executor.map(download_site, sites)
if __name__ == "__main__":
sites = [
"https://www.jython.org",
"http://olympus.realpython.org/dice",
] * 80
start_time = time.time()
download_all_sites(sites)
duration = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Downloaded {len(sites)} in {duration} seconds")
asyncio 모듈
import asyncio
import time
import aiohttp
async def download_site(session, url):
async with session.get(url) as response:
print("Read {0} from {1}".format(response.content_length, url))
async def download_all_sites(sites):
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
tasks = []
for url in sites:
task = asyncio.ensure_future(download_site(session, url))
tasks.append(task)
await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
if __name__ == "__main__":
sites = [
"https://www.jython.org",
"http://olympus.realpython.org/dice",
] * 80
start_time = time.time()
asyncio.run(download_all_sites(sites))
duration = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Downloaded {len(sites)} sites in {duration} seconds")
CPU 바운드 작업 개선하기
순차적 버전
import time
def cpu_bound(number):
return sum(i * i for i in range(number))
def find_sums(numbers):
for number in numbers:
cpu_bound(number)
if __name__ == "__main__":
numbers = [5_000_000 + x for x in range(20)]
start_time = time.time()
find_sums(numbers)
duration = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Duration {duration} seconds")
multiprocessing 모듈
import multiprocessing
import time
def cpu_bound(number):
return sum(i * i for i in range(number))
def find_sums(numbers):
with multiprocessing.Pool() as pool:
pool.map(cpu_bound, numbers)
if __name__ == "__main__":
numbers = [5_000_000 + x for x in range(20)]
start_time = time.time()
find_sums(numbers)
duration = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Duration {duration} seconds")
언제 동시성을 사용
- 반드시 동시성이 필요한 경우(성능 이슈 등)에만 사용을 하자
- 성능 이슈가 CPU 바운드인지 IO 바운드인지 파악
- CPU 바운드는 오직
multiprocessing을 사용해서 개선이 가능 - IO 바운드는 웬만하면
asyncio을 사용하고threading은 꼭 필요할 때만 사용
- CPU 바운드는 오직
